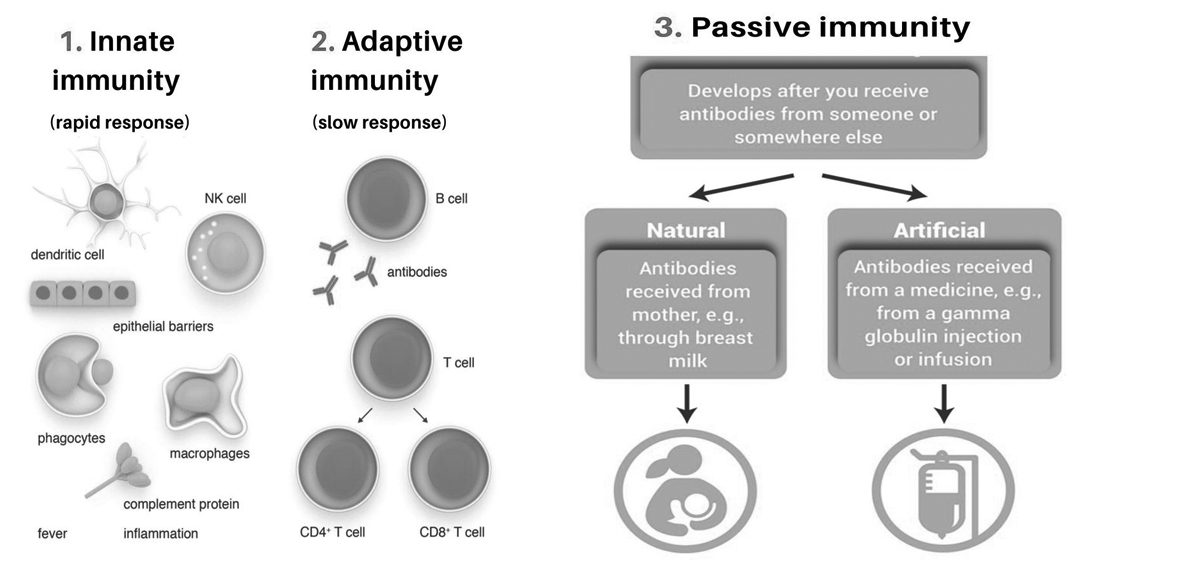
 Innate or Natural immunity:
Innate or Natural immunity:
 Types of innate immunity:
Types of innate immunity:
| NATURAL | ARTIFICIAL | |
| ACTIVE | Natural active immunity occurs when a person develops immunity as a result of exposure to disease organisms or foreign toxins, venoms, allergens or drugs; generally, on initial exposure, the person develops the disease or has an initial negative response to the toxin or venom. | Artificial active immunity occurs when a person develops immunity as a result of exposure to a vaccine designed to protect against disease organisms or foreign toxins, venoms, or allergens; generally, on initial exposure, the person does not develop symptoms of the disease or has only minimal response to the toxin or venom. |
| PASSIVE | Passive active immunity occurs when a mother transmits her own antibodies to her fetus across the placenta or to her infant in her milk; such immunity is transient and relatively short-lived. | Passive artifticial immunity occurs when an individual receives antibodies (injections of gamma globulin) or immune cells (leukocyte transfusions or bone marrow transplants) from another individual (who had had exposure to a specific antigen); such immunity may be transient and relatively short-lived (gamma globulin injections or leukocyte transfusions) or it may be permanent (bone marrow transplants). |
