CLONING- PPP 100 - PRELIMS 2024 - 11
Cloning simply means creating exact replicas or copies. Cloning in biotechnology refers to the process of creating identical copies of either DNA fragments, cells or organisms. The organism which has the identical genetic make-up and the morphological attributes of the source organism is called a clone, while the process is called cloning.
Types of Cloning
Based on the origin of the process, we can have two main types of cloning, i.e. natural cloning and artificial cloning:
- Natural Cloning: Reproduction through asexual and vegetative means result in the development of clones, and thus are examples of natural cloning methods.
a. Plants generally produce clones by vegetative means, while some lower organisms and bacteria reproduce asexually to produce clones.
b. Few examples of asexual reproductive methods are fission, budding, reproduction by asexual spores, fragmentation, etc.
c. Few examples of vegetative reproductive methods are reproduction by rhizomes, runner, corms, bulbs, tubers, offset, stolon, etc.
d. In all these methods/ways, the new organisms (offsprings) formed are the clones of the parent. - Artificial Cloning: Artificial cloning primarily refers to the biotechnological process of creating clones of either DNA fragments or genes or cells or organisms for various purposes. Various techniques have been developed and used based on the entity to be cloned.
Types of Natural Cloning
- Reproductive Cloning in Horticulture: Cloning of an entire organism is known as reproductive cloning.
a. In plants, this happens naturally by vegetative methods.
b. Grapevine propagation by cuttings is an age-old example of organism cloning in horticulture.
c. Apomixis is another natural way of creating genetically identical organisms.
d. Apomixis is defined as reproduction without fertilization.
e. Replacement of seeds by plantlets and replacement of flowers by bulbils are considered types of apomixis.
f. Some vascular plants like dandelions and some grasses form seeds asexually by apomixis and form clonal populations which are genetically identical to the parent plant. - Organism Cloning by Parthenogenesis: Natural organism cloning exists in nature in some animals which reproduce by parthenogenesis.
a. Parthenogenesis is the development of an organism without fertilization of gametes.
b. Such organisms that develop through parthenogenesis are genetically identical to the mother.
c. Few examples of animals where reproduction by parthenogenesis takes place are insects like honeybees, wasps, some crustacean species, nematodes, and lizards (komodo dragon). - Cellular Cloning: Creating a population of cells from a single-parent cell is referred to as cellular cloning.
a. Unicellular organisms like bacteria and yeast exhibit the simplest form of cellular cloning, and in this case, just a single-cell inoculation is required into the nutrient medium.
Types of Artificial Cloning
1. Molecular Cloning: It is also referred to as gene cloning or DNA cloning.
a. The branch of biology that deals with such molecular cloning is called genetic engineering or recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology.
b. A fragment of DNA or gene is replicated into a number of identical copies.
c. DNA fragments containing whole genes or part of genes or other regulatory elements such as promoters are amplified.
d. The cloned products are used in genetic engineering, from sequencing the fragments to protein production.
e. There are two approaches to perform molecular cloning.
f. One approach uses live organisms like bacteria and plasmids. DNA fragments are inserted into natural or artificial cloning vectors, and then these vectors are replicated in host organisms like bacteria, animal or plant cells.
g. Another approach of amplifying the DNA fragments is more techno-chemical and does not need living organisms.
h. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the most common technique used for molecular cloning, and it relies on the thermal cycling of DNA fragments and enzyme driven DNA replication.
|
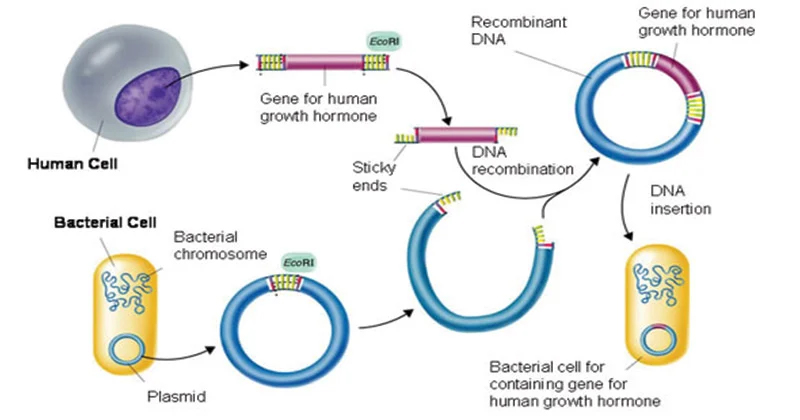
Recombinant DNA technology (RDT), often referred to as Genetic Engineering, is an in-vitro (lab) method of manipulating genes (DNA fragments) by using a set of tools and techniques. The primary aim of RDT is to produce “Transgene (recombinant DNA) and its product (recombinant protein), to be applied across different fields of biotechnology. The RDT is a continuously evolving technology due to the advancement in its tools and techniques, such as the discovery of the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing tool. Tools of Recombinant DNA TechnologyThe following are the tools employed in the process involved in Recombinant DNA Technology:
Process involved in Recombinant DNA TechnologyRecombinant DNA technology undergoes through the following steps:
Applications of Recombinant DNA TechnologyRecombinant DNA Technology stands as a cornerstone of modern science with far-reaching applications across numerous fields.
|
2. Reproductive Cloning
a. When the whole organism is cloned, it is referred to as reproductive cloning.
b. An identical copy or clone of an entire multicellular organism is made in this process.
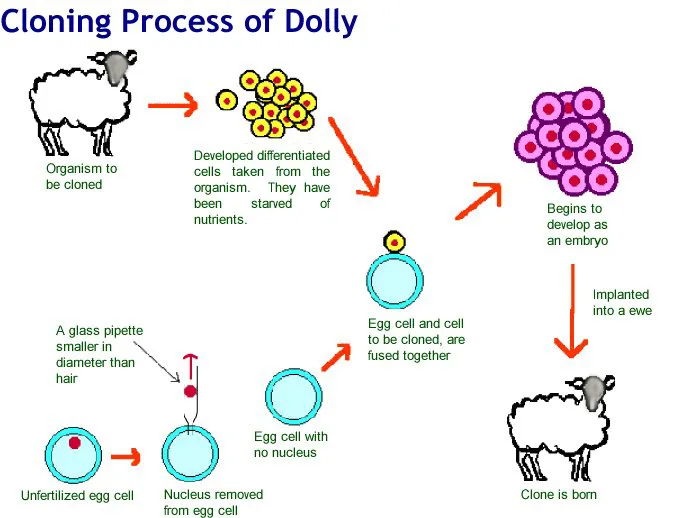
c. Breakthrough in reproductive cloning came when Dolly was cloned using a technique called somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT).
d. To explain this technique briefly, the nucleus from a somatic cell of an adult donor is removed and inserted into an enucleated (whose nucleus has been removed) egg cell or early blastocyst cell.
e. Once the nucleus is inside the egg cell or blastocyst cell, the cell is stimulated with mild electric current for division.
f. As the cell divides, it develops into an embryo. This cloned embryo is a genetically identical copy of the original organism.
g. Reproductive cloning has been successfully performed in a number of species.
h. Few examples of organisms where reproductive cloning is successful are tadpole, zebrafish, pig, cat, rat, mice, mule, horse, dog, Pashmina goat, macaque monkey, etc.
|
Early experiments on reproductive cloning began some 40 years ago through a process known as embryo splitting. In this procedure, a single two-celled stage embryo was split manually into two cells, and then each cell was grown as an identical embryo. In 1924, Hans Spemann and his student Hilde Mangold performed some experiments of somatic cell nucleus transfer (SCNT) in amphibian embryos. This was considered the first step towards animal cloning. In 1996, Ian Wilmut and his team announced the successful cloning of a sheep, Dolly. This was a major breakthrough. Dolly was cloned using the same technique of somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT). The cloning of Dolly was significant because she was the first mammal to be cloned successfully using an adult somatic cell. The birth of Dolly was also significant because it demonstrated that a nucleus could be dedifferentiated and redesigned to develop into a new organism.
|
- Therapeutic Cloning
a. Cloned embryos are used to get stem cells from them for research and therapeutic usage.
b. Stem cells can be dedifferentiated into more than 200 types of cells.
c. Cloned stem cells are genetically identical to the patient and hence can be grafted in the patient’s body without risk of rejection by the immune system.
d. Embryos are not implanted into the uterus.
e. Examples of diseases treated with cloned stem cells are Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, diabetes mellitus, spinal injury, etc.
f. Cloned stem cells are also used to study normal or abnormal embryo development and to know if drugs are toxic or cause any birth defects.
Stem Cell Therapy:
- Stem cell therapy is a form of regenerative medicine designed to repair damaged cells within the body by reducing inflammation and modulating the immune system.
- This phenomenon makes stem cell therapy a viable treatment option for various medical conditions.
- It can be used to treat a variety of medical conditions, such as autoimmune, inflammatory, and neurological disorders.
Stem cells
- Stem cells are cells from which all other cells, with their respective specialised functions, are generated.
- The human body, under certain conditions, “divides” stem cells to either create new stem cells or cells with specific functions, such as blood cells, brain cells, bone cells, muscle cells, etc.
Sources of Stem cells:
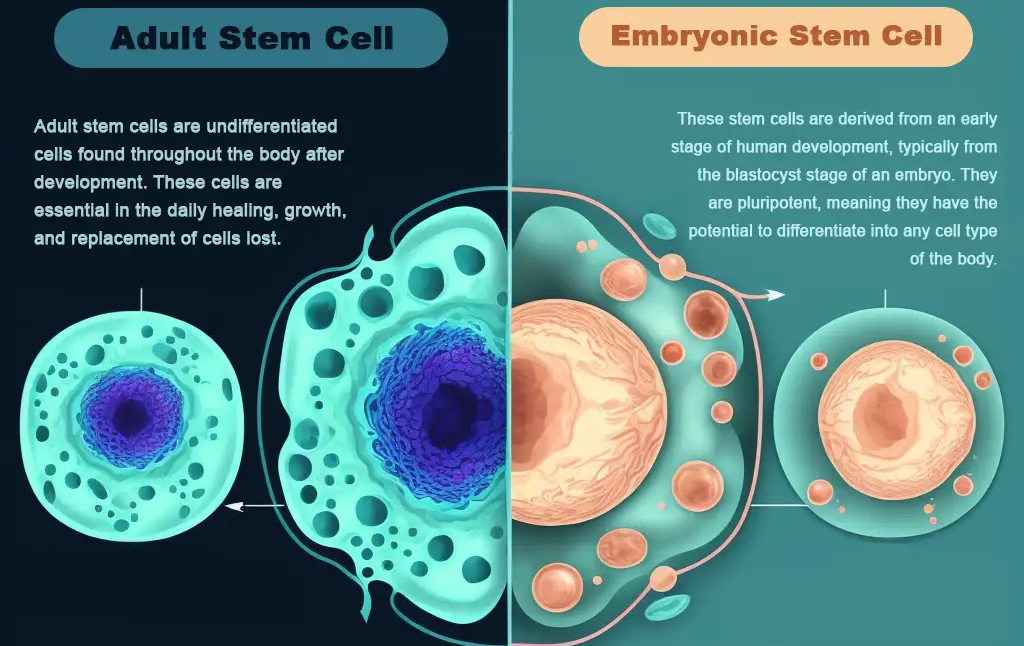
- Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs): These are derived from early-stage embryos and have the potential to become any cell type in the body.
- However, their use is ethically controversial and strictly regulated in many countries.
- Adult Stem Cells: These are found in specific tissues and organs throughout the body and play a role in tissue maintenance and repair.
- For Example: It includes hematopoietic stem cells (found in bone marrow) and mesenchymal stem cells (found in various tissues like bone, fat, and dental pulp).
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): These are adult cells that have been reprogrammed to behave like embryonic stem cells.
- They can be generated from a patient’s own cells, reducing the risk of rejection.
Applications of Stem Cell Therapy:
- Regenerative Medicine: Repairing or replacing damaged tissues and organs, such as heart muscle, cartilage, or nerve cells.
- Treatment of Chronic Diseases: Exploring potential treatments for conditions like diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and spinal cord injuries.
- Immune Disorders: Modifying or enhancing the immune system to fight cancer or autoimmune diseases.
- Orthopedics: Treating orthopedic injuries and conditions like osteoarthritis.
- Cosmetic Procedures: Using stem cells for procedures like facial rejuvenation.
Menstrual Blood Stem Cells
- Menstrual blood-derived stem cells (MenSCs), known asendometrial stromal mesenchymal stem cells, possess multipotent properties, meaning they can differentiate into various tissue types such as fat cells, bone cells, and smooth muscle cells.
- MenSCs are an ethical source of adult stem cells that can be collected painlessly from women.
- MenSCs can be collected through amenstrual cup, providing a less invasive alternative to surgical biopsies.
- MenSCs can be obtained from women''s menstrual blood derived from the endometrium(lines the inside of the uterus).
- Role in Women''s Health:
- Regenerative Potential:
- MenSCs exhibit multipotent characteristics. This means they can differentiate into various cell types, including neurons, cartilage, fat, bone, heart, liver, and skin cells.
- Treating Endometriosis:
- MenSCs offer potential avenues for treating gynaecological disorders such as endometriosis and infertility.
- Endometriosisis a disease in which tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus. It can cause severe pain in the pelvis and make it harder to get pregnant.
- Endometriosis can start at a person''s first menstrual period and last until menopause (end of menstrual cycles).
- Common symptoms of endometriosis includepelvic pain, especially during menstruation, painful intercourse, infertility, heavy menstrual bleeding, and gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhoea or constipation.
- The cause and ways to prevent endometriosis are unknown. There is no cure, but its symptoms can be treated with medicines or, in some cases, surgery.
- The contributing factor to endometriosis is the backflow of menstrual blood into a woman''s fallopian tubes.
- This backward flow carries blood into thepelvic cavity, a funnel-shaped space between the bones of the pelvis.
- Endometrial stem cells deposited in these areas may prompt the growth of endometrial-like tissueoutside the uterus, resulting in painful lesions, scarring, and often infertility.
- Broader Therapeutic Applications:
- Menstrual stem cells have potential therapeutic applications beyond gynaecological diseases.
- Injecting menstrual stem cells into diabeticmice stimulated the regeneration of insulin-producing cells and improved blood sugar levels.
- Treating injuries with stem cells or their secretions helped heal wounds in mice.
- Menstrual stem cells can be transplanted into humans without adverse side effects.
- Challenges:
- Despite the convenience of collecting menstrual stem cells, research in this area represents a tiny fraction of overall stem cell research.
- As of 2020, menstrual stem cell researchaccounted for only25% of all mesenchymal cell research, while bone marrow stem cells represented 47.7%.
- Ensuring consistent and scalable production of MenSCsfor clinical applications remains a challenge.
- Cultural taboos and limited investment in women’s health research pose significant challenges in securing funding for menstrual stem cell studies.
- Addressinggender bias in research funding is crucial to elevate menstrual stem cell research as a promising frontier in regenerative medicine, beyond its association with menstruation.
- Despite the convenience of collecting menstrual stem cells, research in this area represents a tiny fraction of overall stem cell research.
- Endometriosisis a disease in which tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus. It can cause severe pain in the pelvis and make it harder to get pregnant.
- MenSCs offer potential avenues for treating gynaecological disorders such as endometriosis and infertility.
- Regenerative Potential: