National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM)
NCMM
- Genesis: In Budget for 2024-25, establishment of Critical Mineral Mission was announced.
- Key Objective: To secure India''s critical mineral supply chain by ensuring mineral availability from domestic and foreign sources.
- Coverage: It will encompass all stages of the value chain, including mineral exploration, mining, beneficiation, processing, and recovery from end-of-life products.
- Key Features:
- It will offer financial incentives for critical mineral exploration and promote the recovery of these minerals from overburden and tailings.
- It aims to create a fast track regulatory approval process for critical mineral mining projects.
- It will encourage Indian PSUs and private sector companies to acquire critical mineral assets abroad and enhance trade with resource-rich countries.
- It proposes development of stockpile of critical minerals within the country.
- It includes provisions for setting up of mineral processing parks.
- Mining in offshore areas (Polymetallic nodules contain minerals like Cobalt, REE, etc.)
- Governance Framework:
- Activities will be coordinated by the Empowered Committee on Critical Minerals.
- Ministry of Mines will be the administrative Ministry.
The Mission will follow a whole-of-government approach which means it will work closely with relevant ministries, PSUs, private companies, and research institutions to achieve its objectives.
India’s net import dependency of Critical mineral
|
Critical Mineral |
Percentage dependency |
Major Import Sources (2020) |
|
Lithium |
100% |
Chile, Russia, China, Ireland, Belgium |
|
Cobalt |
100% |
China, Belgium, Netherlands, US, Japan |
|
Nickel |
100% |
Sweden, China, Indonesia, Japan, Philippines |
|
Vanadium |
100% |
Kuwait, Germany, South Africa, Brazil, Thailand |
|
Niobium |
100% |
Brazil, Australia, Canada, South Africa, Indonesia |
|
Germanium |
100% |
China, South Africa, Australia, France, US |
|
Rhenium |
100% |
Russia, UK, Netherlands, South Africa, China |
|
Beryllium |
100% |
Russia, UK, Netherlands, South Africa, China |
|
Tantalum |
100% |
Australia, Indonesia, South Africa, Malaysia, US |
|
Strontium |
100% |
China, the US, Russia, Estonia, Slovenia |
|
Zirconium(zircon) |
80% |
Australia, Indonesia, South Africa, Malaysia, US |
|
Graphite(natural) |
60% |
China, Madagascar, Mozambique, Vietnam, Tanzania |
|
Manganese |
50% |
South Africa, Gabon, Australia, Brazil, China |
|
Chromium |
2.5% |
South Africa, Mozambique, Oman, Switzerland, Turkey |
|
Silicon |
<1% |
China, Malaysia, Norway, Bhutan, Netherlands |
Critical Minerals
- Definition: Critical minerals are minerals which are essential for economic development and national security of any country. The lack of availability or concentration of existence, extraction or processing of these minerals in few geographical locations may lead to supply chain vulnerability and disruption.
|
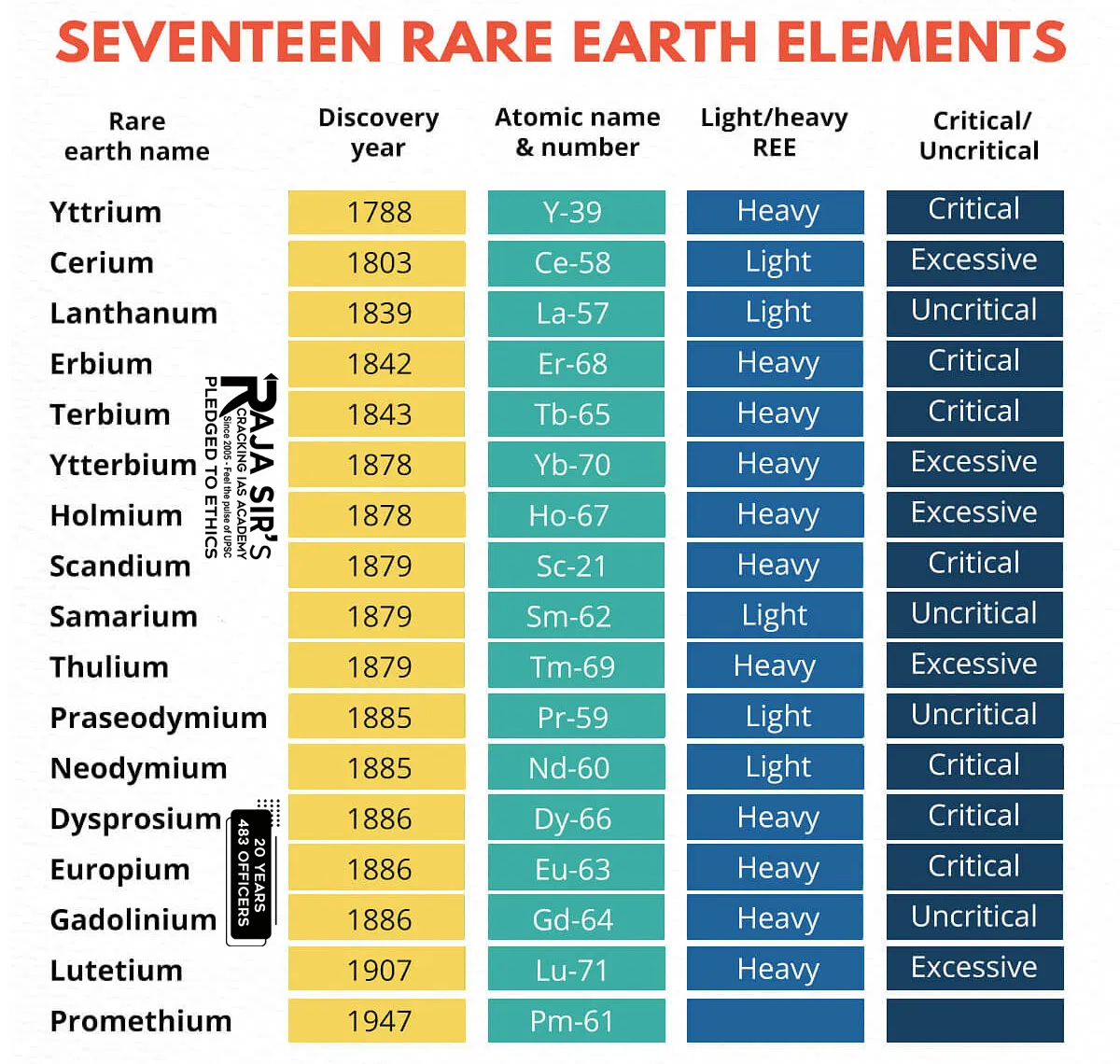
Economic Importance + Supply Risk = Criticality of Minerals PGE Group of Elements refers to Platinum Group Elements—namely platinum (Pt), palladium (Pd), rhodium (Rh), ruthenium (Ru), iridium (Ir), and osmium (Os). These six rare metals share similar physical and chemical properties, such as high melting points and excellent catalytic qualities, and are found together in specific mineral deposits often associated with nickel and copper deposits. They are important for high-technology sectors, including automotive (catalytic converters), electronics, and medical equipment. Rare Earth Elements (REEs)
|
- India has released a list of 30 critical minerals for India including Bismuth, Cobalt, Copper, Phosphorous, Potash, Rare Earth Elements (REE), Silicon, Tin, Titanium, etc.
- Currently, India has heavy reliance on imports of critical minerals.
|
Significance of Critical Minerals |
||||
|
Environment
|
National Security
|
Economic & Electronic
|
||
|
Six Critical Elements Opened for Private Mining Lithium
Properties
Occurrence
Global Reserves and Production
Uses
Titanium
Zirconium
Beryllium
Niobium
Tantalum
|
||||
Roadblocks to India''s Critical Mineral Security
- Limited Domestic Reserves: India does not have many critical mineral reserves, or its requirements may be higher than the availability.
- E.g., currently, there are no working mining leases for cobalt, nickel, lithium, and neodymium for production purposes.
- Challenges in Exploration: Many critical minerals are deep-seated, requiring high-risk investments in exploration and advanced mining technologies.
- E.g. Presence of 5.9 million tonnes lithium deposits in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Supply chain Disruptions: Production and processing of many critical minerals are geographically concentrated, making global supply vulnerable to several risks.
- China controls 60% of rare earth production, 60% of critical minerals production and 80% of the processing worldwide.
- In 2024, China banned exports of gallium, germanium, antimony, and other key materials to US (weaponising critical mineral exports).
- Democratic Republic of Congo supplies ~70% of the world''s cobalt, but political instability has led to supply disruptions.
- Environmental Concerns: Mining and processing of critical minerals often have significant environmental footprint resulting in protests from local population and environmental groups.
- E.g., An estimated 54% of critical materials lie near indigenous people''s land. (International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA))
- Inadequate recycling infrastructure: Recycling of critical minerals from e-waste is underdeveloped, with the sector remaining largely unorganized and inefficient.
|
Other Initiatives taken for critical Minerals Policy and Regulatory Framework
Exploration and Domestic Production
International Collaborations & Trade Agreements
|
Strategies for long-term critical mineral security
- Strengthening Domestic Critical Mineral Production:
- Exploring alternative allocation mechanisms to attract more private investment, such as granting exploration companies the right to mine the minerals they discover.
- Increase public and private investment in geological surveys, exploration technologies, etc.
- Developing Domestic Processing Capabilities: Provide financial incentives, tax breaks, and other policy support to encourage private and public sector companies to invest in processing facilities.
- Special Economic Zones (SEZs) focused on critical mineral processing can be established.
- Need for Robust Global Cooperation: Strengthening bilateral and multilateral partnerships with mineral-rich countries and other key stakeholders to secure access to critical mineral supplies.
- Develop a Comprehensive Critical Minerals Strategy (CMS): It can help focus on priority concerns in supply risks, domestic policy regimes, and sustainability.
- Conduct periodic detailed assessments of India''s critical mineral needs across various sectors.
- Setting up state-of-the-art e-waste recycling facility, introducing a nationwide "Recycle for Resources" campaign to increase public awareness and participation in e-waste recycling, etc.
- Diversifying import sources from various countries.
- Role of State Government: Infrastructure Development- Develop transportation, power, and storage infrastructure near Critical Mineral mining areas, etc.
Securing critical minerals is crucial for India''s economic growth, energy transition, and national security. Strengthening domestic mining, refining, and recycling, along with a robust National Critical Minerals Strategy, will help reduce import dependence and ensure long-term supply stability.