 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
Article 32 empowers the supreme court to issue writs for the protection of fundamental rights in case of violation because of this authority to issue directions or orders for the execution of any of the rights conferred by the constitution The Supreme Court is made ''the protector and guarantor of Fundamental Rights''. A writ is a formal, legal document issued by the executive or judicial body which commands an individual or entity to do or refrain from doing a particular act. It can be in the form of orders, warrants, directions, summons, etc. The aggrieved person applies for issuance of a writ through presenting a writ petition before the competent authority. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar remarked Article 32 as the heart and soul of the constitution.
Types of Writs
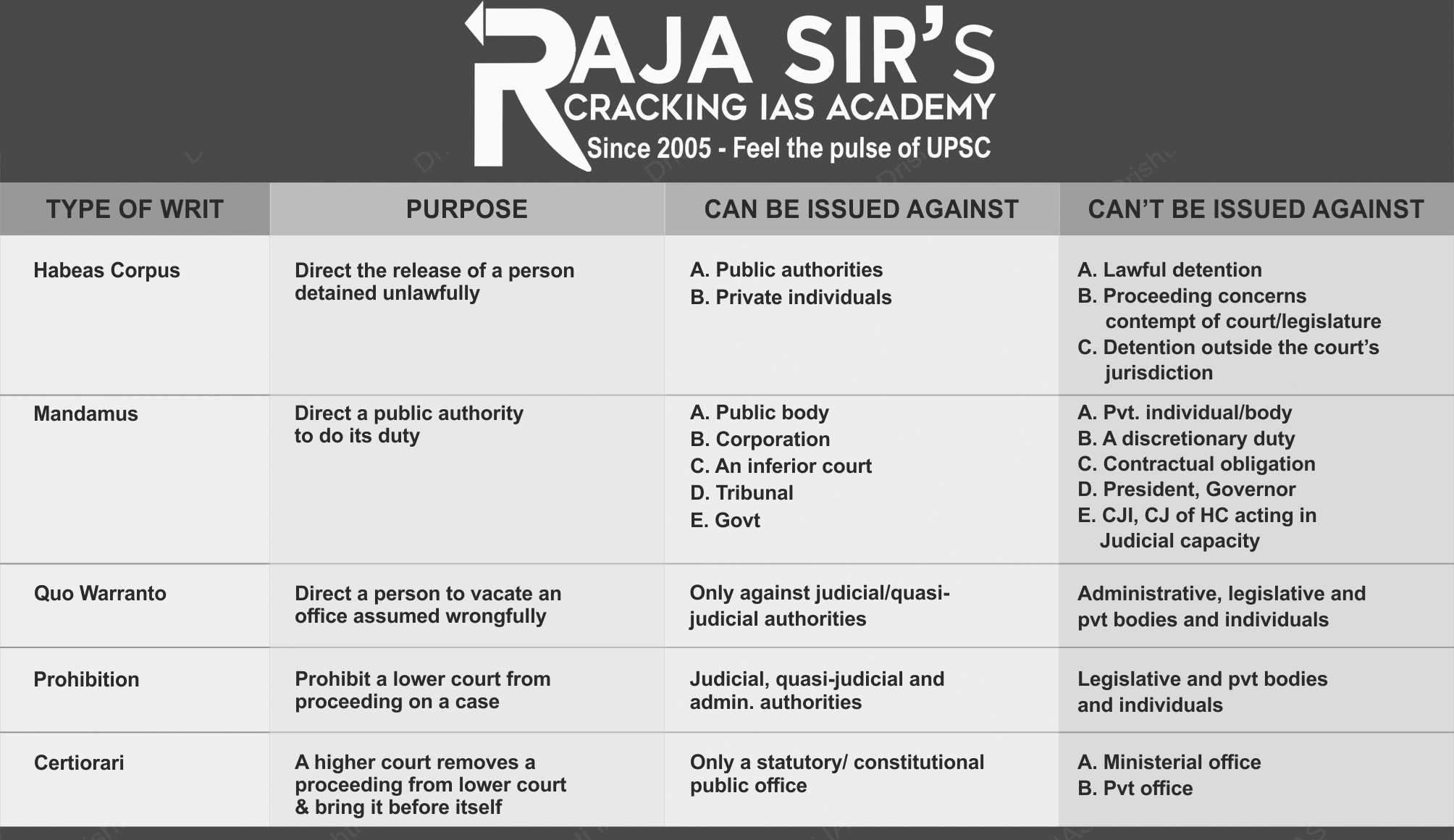
Significance of Article 32
Limitations of Article 32
While Article 32 has certain limitations, it plays a crucial role in protecting the rights of individuals and upholding the principles of justice and equality. Article 32 is often regarded as the "heart and soul" of the Indian Constitution.
 General Studies
General Studies Political Science and International Relations
Political Science and International Relations