|
Subcritical, Critical, Supercritical When a U-235 atom splits, it usually gives off two or three neutrons. If there are other U-235 atom nearby, then one of three things happens:If exactly 1 free neutrons from each fission hits another U-235 nucleus and causes it to split, then the mass of Uranium is said to be critical. The mass will exist at a stable temperature. A nuclear reactor must be maintained in a critical state. If less than one of the free neutrons hits another U-235 atom, then the mass is subcritical. Eventually, induced fission will end in the mass.If more than one of the free neutrons hits another U-235 atom, then the mass is supercritical. It will heat up. In a nuclear reactor, the reactor core needs to be slightly supercritical so that the plant operators can raise and lower the temperature of the reactor. The control rods give the operators a way to absorb free neutrons so that the reactor can be maintained at a critical level. 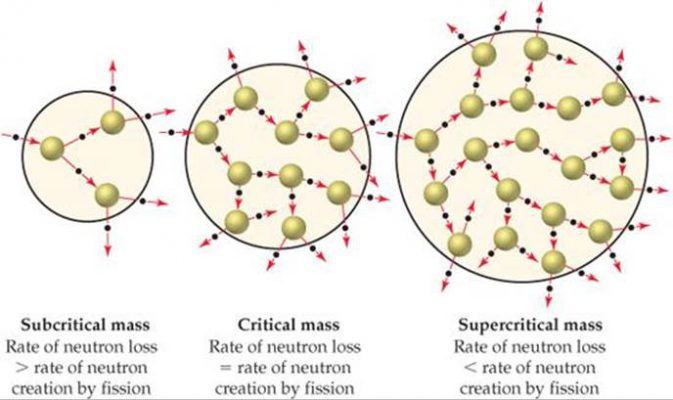 |
 General Studies
General Studies Political Science and International Relations
Political Science and International Relations